Environments
Switch to Environments view using the
icon in the main menu.
Environment Variables
Section titled “Environment Variables”Environment variables are key-value pairs that store configuration data outside of your application code. In apps built with Draftbit, environment variables are injected into your app at build time. This means they’re available throughout your app code, but they’re not included in your source code repository, keeping sensitive data secure.
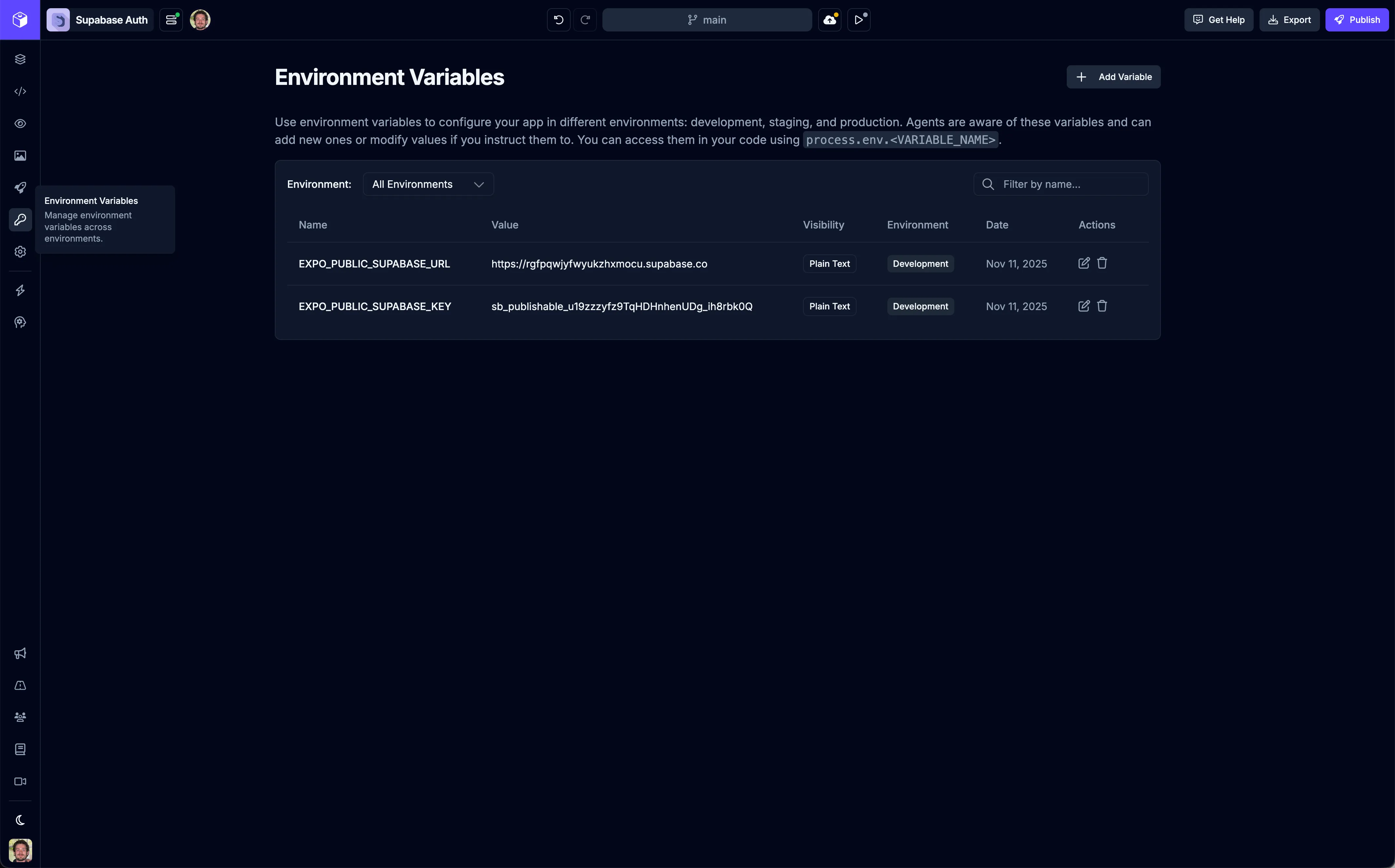
These variables can be used to:
- Store API keys and secrets - Keep sensitive credentials out of your codebase
- Configure API endpoints - Use different backend URLs for development vs production
- Set feature flags - Enable or disable features based on the environment
- Manage app configuration - Store app IDs, bundle identifiers, and other build settings
Adding Environment Variables
Section titled “Adding Environment Variables”To add a new environment variable to your app project, navigate to the Environments page and click the ![]() button to open the environment variable form.
button to open the environment variable form.
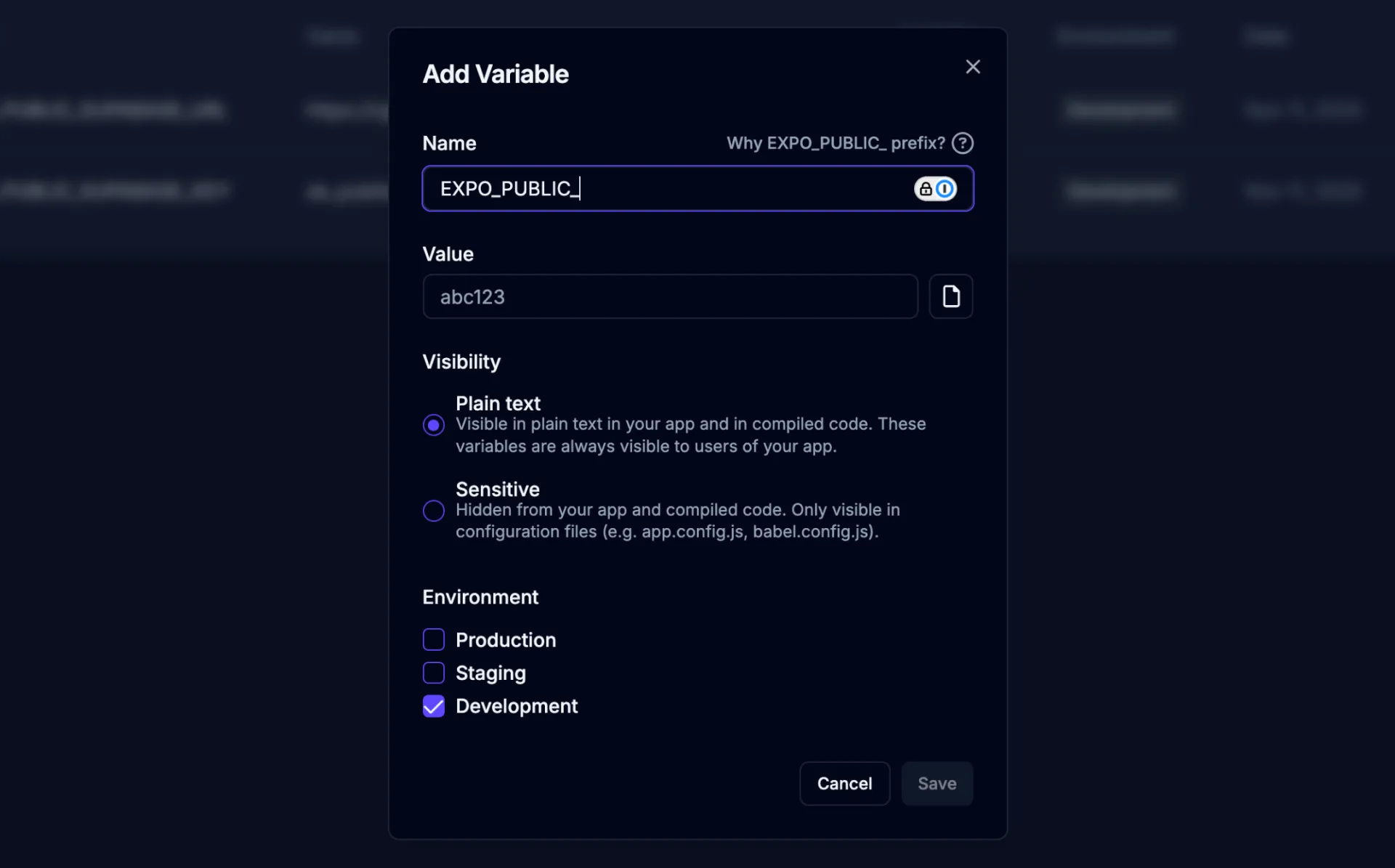
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of your environment variable. This should be uppercase and use underscores instead of spaces (e.g., |
| Value | The actual value for your environment variable. This can be a URL, API key, string, number, or any other configuration value your app needs. For sensitive values like API keys or secrets, the value will be masked in the UI after you save it for security purposes. |
| Visibility | Controls how the environment variable is included in your app. See the Visibility Settings section below for details on each option. |
| Environments | Select which environments this variable should be available in. You can choose one or more of: Development, Staging, and Production. This allows you to use different values for the same variable name across different environments (e.g., different API endpoints for development vs production). |
After filling in all required fields, click the Save button to create the environment variable. Once created, it will be available in your app builds and can be accessed in your code using process.env.VARIABLE_NAME.
Visibility Settings
Section titled “Visibility Settings”Environment variables in Draftbit support two visibility levels that control how the variables are included in your app.
| Visibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Plain text | Visible in plain text in your app and in compiled code. These variables are always visible to users of your app. Use this setting for non-sensitive configuration values like public API endpoints, feature flags, or other settings that don’t contain secrets or credentials. |
| Sensitive | Hidden from your app and compiled code. Only visible in configuration files (e.g. |
Using Environment Variables
Section titled “Using Environment Variables”Once you’ve added environment variables in the Environments page, you can access them in your app code or reference them in the AI Agent chat.
Variables in code
Section titled “Variables in code”When using environment variables in your app code, you can access them using process.env.VARIABLE_NAME. However, the visibility setting you choose affects how these variables are included:
- Plain text variables are accessible in your app code using
process.env.VARIABLE_NAMEand will be visible in your compiled app code. - Sensitive variables are only available in configuration files like
app.config.jsandbabel.config.js, and are not included in your compiled app code.
For example, with plain text variables:
// Access a plain text environment variableconst apiBaseUrl = process.env.API_BASE_URL;
// Use in API callsfetch(`${apiBaseUrl}/users`);Plain text environment variables are visible in your compiled app code, meaning anyone can inspect your app and see these values. Never use plain text visibility for sensitive data like API keys or passwords.
Sensitive variables are typically used in configuration files during the build process, such as setting app IDs or bundle identifiers, but are not accessible in your runtime app code.
Variables in chat
Section titled “Variables in chat”You can reference your environment variables when chatting with the AI Agent in the Builder. The agent has access to your environment variables and can use them when building features or making changes to your app.
When you mention an environment variable in your chat messages, the agent will automatically use the correct variable name and can help you integrate it into your code. For example, you might say:
- “Use the
EXPO_PUBLIC_API_BASE_URLenvironment variable for all API calls” - “Create a function that uses
EXPO_PUBLIC_STRIPE_PUBLIC_KEYto initialize Stripe” - “Update the login screen to use the
EXPO_PUBLIC_AUTH_ENDPOINTvariable” - “Initialize Supabase using
EXPO_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_URLandEXPO_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_KEY”
The AI Agent understands your environment variable names and will reference them correctly in the code it generates. This makes it easy to build features that rely on your environment-specific configuration without having to manually edit code.
Learn More
Section titled “Learn More”For more detailed information about how environment variables work in Expo apps, including advanced configuration options, multiple .env files, and migration guides, see the Expo documentation on environment variables.